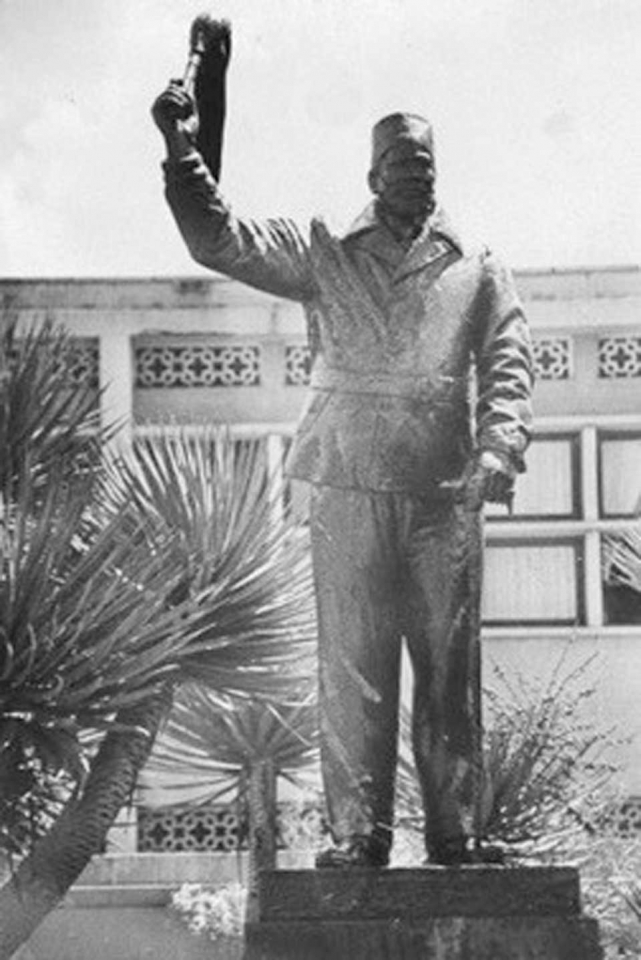
The two statues
Walking around the rest of Nairobi’s city centre one comes across other statues that have no viewing restrictions. I comment on two of these that resonate, in a particular way, with the narrative of founding postcolonial Kenya: Kenyatta’s 1973 and Kimathi’s 2007 statues.
Kenyatta (c.1894-1978) the first president and founding father of postcolonial Kenya, had a second statue made out of cast iron, by James Butler, a British national. It was finished in 1969, shipped to Kenya and unveiled in 1973. It depicts Kenyatta wearing the robes of a university chancellor –he was the chancellor of University of Nairobi from 1970 to 1978. It stands in City Square.
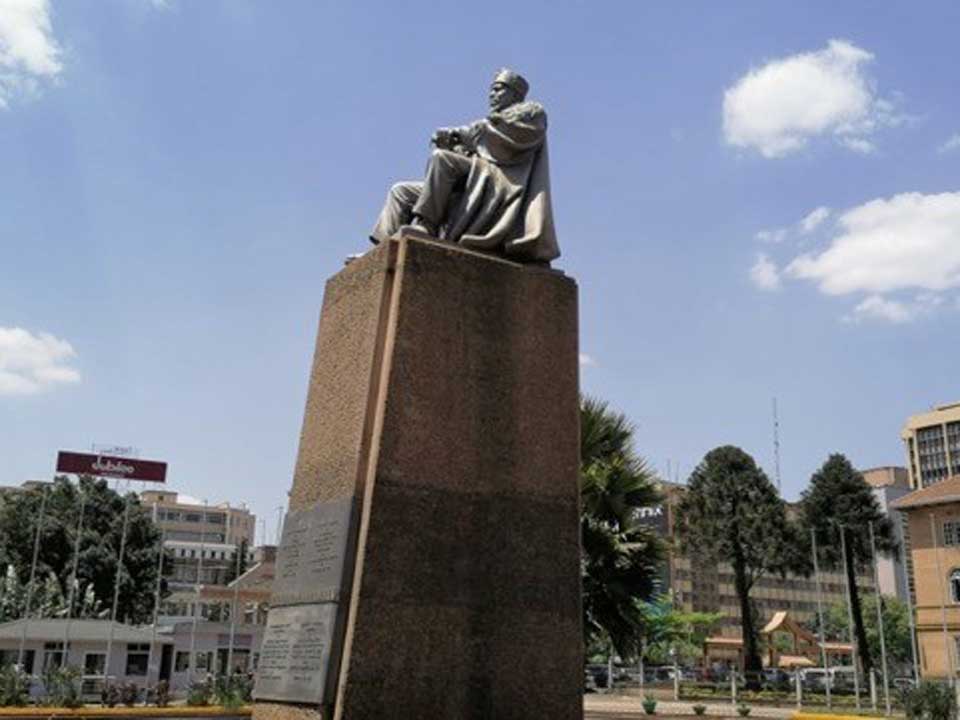

Figure 2. James Butler, Jomo Kenyatta, Nairobi, City Square, 1969 (unveiled in 1973), Bronze, 750 cm © Lydia Muthuma
Kimathi (1920-1957) also has a statue installed along Kimathi Street. He is the self proclaimed Field Marshal of the anti colonial Kenya Land and Freedom Army (KLFA) colloquially known as the Mau Mau. This movement was proscribed in colonial times and during the era of the first and second presidents of Kenya (1952-2003). But in 2003, Kenya’s third president, Mwai Kibaki, eventually unbanned Mau Mau and commisioned a statue in honour of Kimathi. The sculptor, Kevin Oduor, at the invitation of Kenyatta University's Department of Fine Art, made this statue.
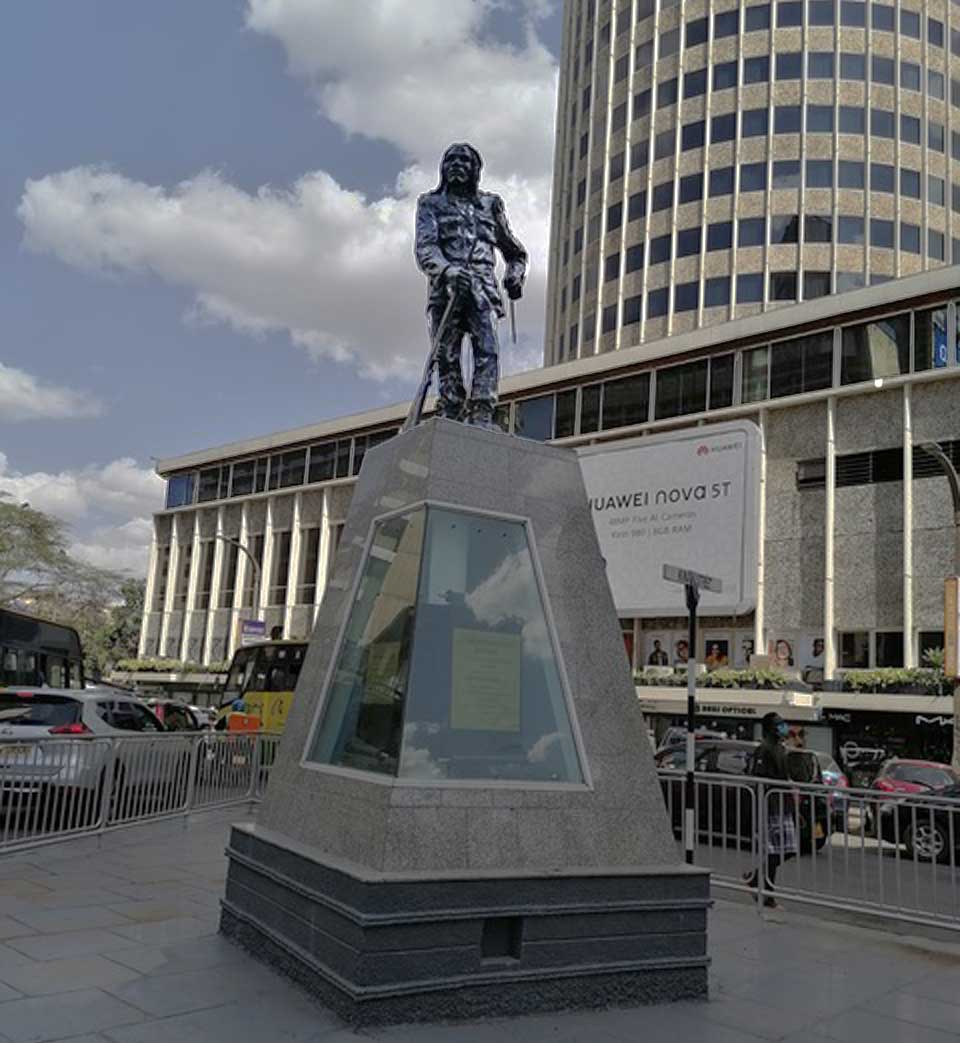

Figure 3. Kevin Oduor, Dedan Kimathi, 2006 (unveiled in 2007), Bronze, 450 cm © Lydia Muthuma
The two statues (excluding the 1964 one) have similarities and differences that can be considered within the context of political history or through the artistic lens since they form part of Nairobi’s visual urban landscape. These statues represent two political figures, considered national heroes and therefore meriting public showing. Mass and volume, employed as the basic building blocks, are used to express emotional energy in a bid to engage the viewer’s affects. The chosen site of each statue (the situ) mediates the public’s affects.
Siting the statues
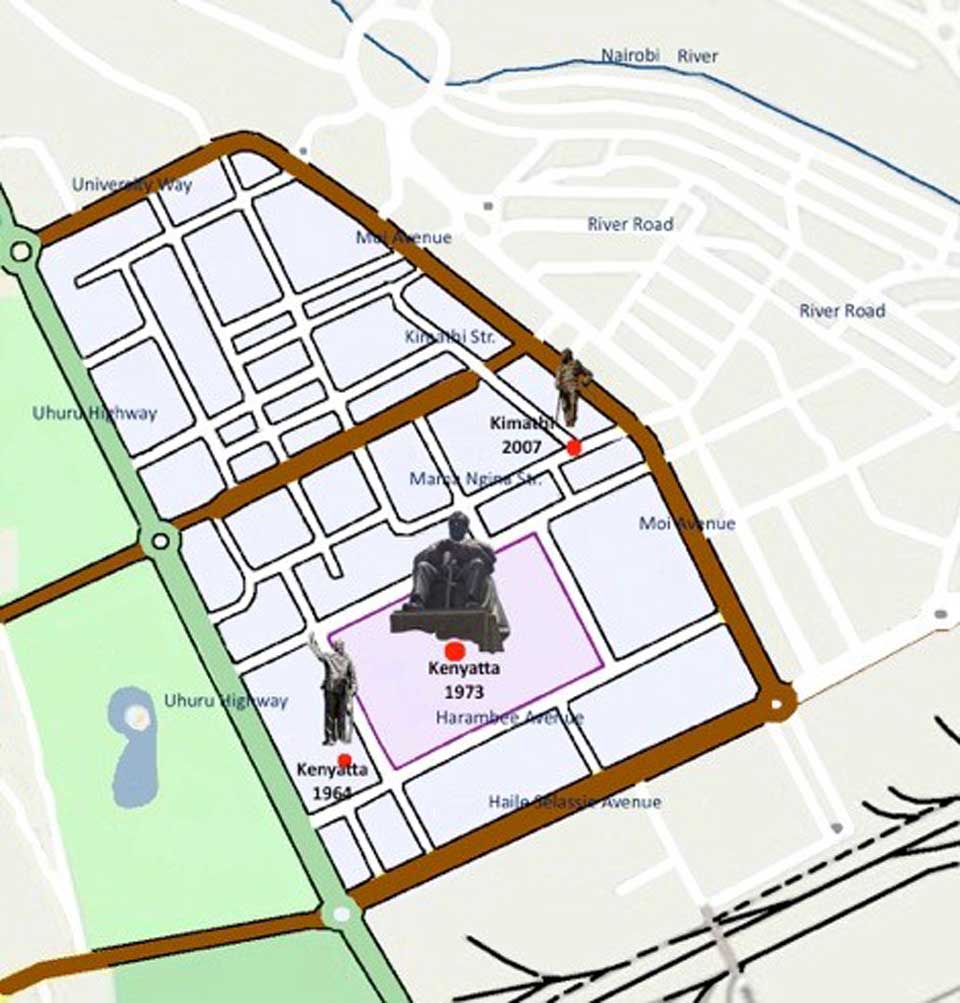
Figure 4. Location of the different statues © Lydia Muthuma
Jomo Kenyatta’s 1973 statue is placed in City Square with about one acre of land setting him apart from the surrounding buildings. Anyone walking into City Square, walks into this statue because it is the focal point. In traversing the square or accessing nearby buildings, one must pay visual homage to Kenyatta’s 1973 statue because of its setting; the geographical centre of the square (cf. figure 4 & 5).
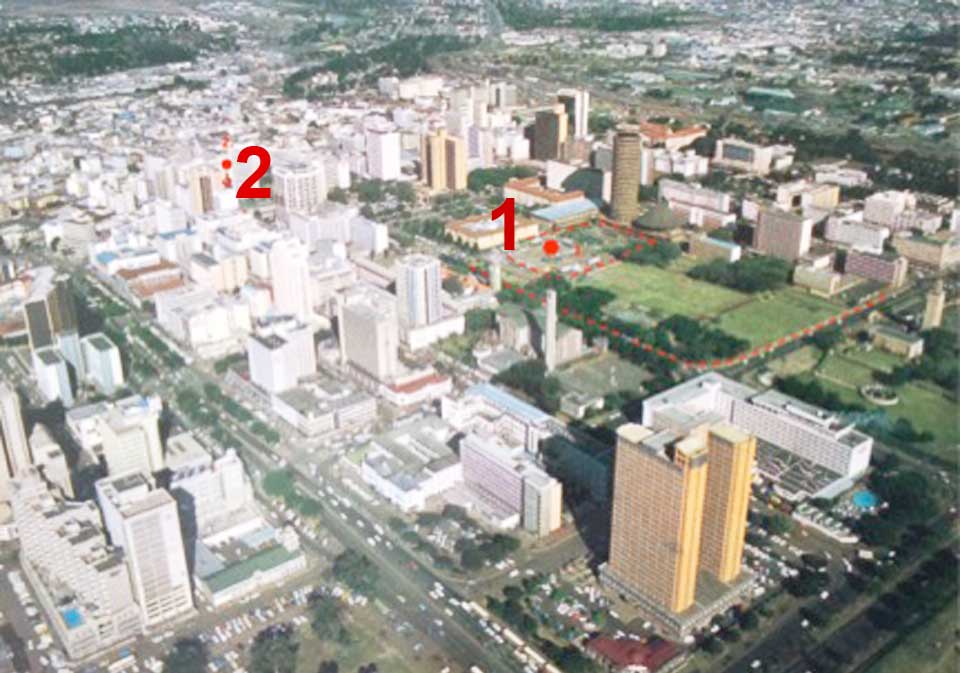
Fig. 5 City Square
Kimathi’s statue is set in different surroundings. By the year 2007 when Kimathi’s statue was installed, empty 1-acre plots, other than City Square, were not to be had in Nairobi’s centre. In fact a heroes' corner was designated about 5 km due west, in 2006, but was deemed unsuitable for Kimathi's statue. The street named for him, right in the middle of the city, was the preferred site. So on a tall plinth, Kimathi stands at the southern end of Kimathi Street. (cf. figure 4 & 5) There is hardly any viewing distance because Kimathi’s statue stands on a tiny traffic island, amidst tall buildings like Corner House (15 stories) and the Hilton Hotel (20 stories). The statue is in the middle of a busy traffic junction – where Mama Ngina Street meets Kimathi Street. And because it is immersed in both vehicular and pedestrian traffic, viewers are treated to short interrupted glances of Kimathi, atop a pyramid-like plinth that was designed by members of Kenyatta University’s Department of Fine Art. Fleeting, staccato snap shots that punctuate the flowing vehicular traffic comprise the everyday viewing experience. Lack of space, attendant hubbub and noise are inextricably bound up with Kimathi’s statue.
Meanwhile ample space and limited, if any, vehicular or pedestrian traffic, are the elements surrounding Jomo Kenyatta’s 1973 statue. He is represented twice life size to Kimathi’s mere life size. Unlike Kimathi, Kenyatta sits comfortably on a tall rectangular plinth. No wonder some say of Kenyatta's 1973 statue, “he is majestic, aloof...”, they are responding to—among other factors— the viewing experience, the physical placement and context of this sculpture. (cf. Figure 4 & 5)
Through the artistic lens
Statues of great men are often linked to significant historical happenings. Investigating their historical context is one way of ‘reading’ them. But it is not the only one. They can also be viewed as artistic components of the landscape they inhabit.
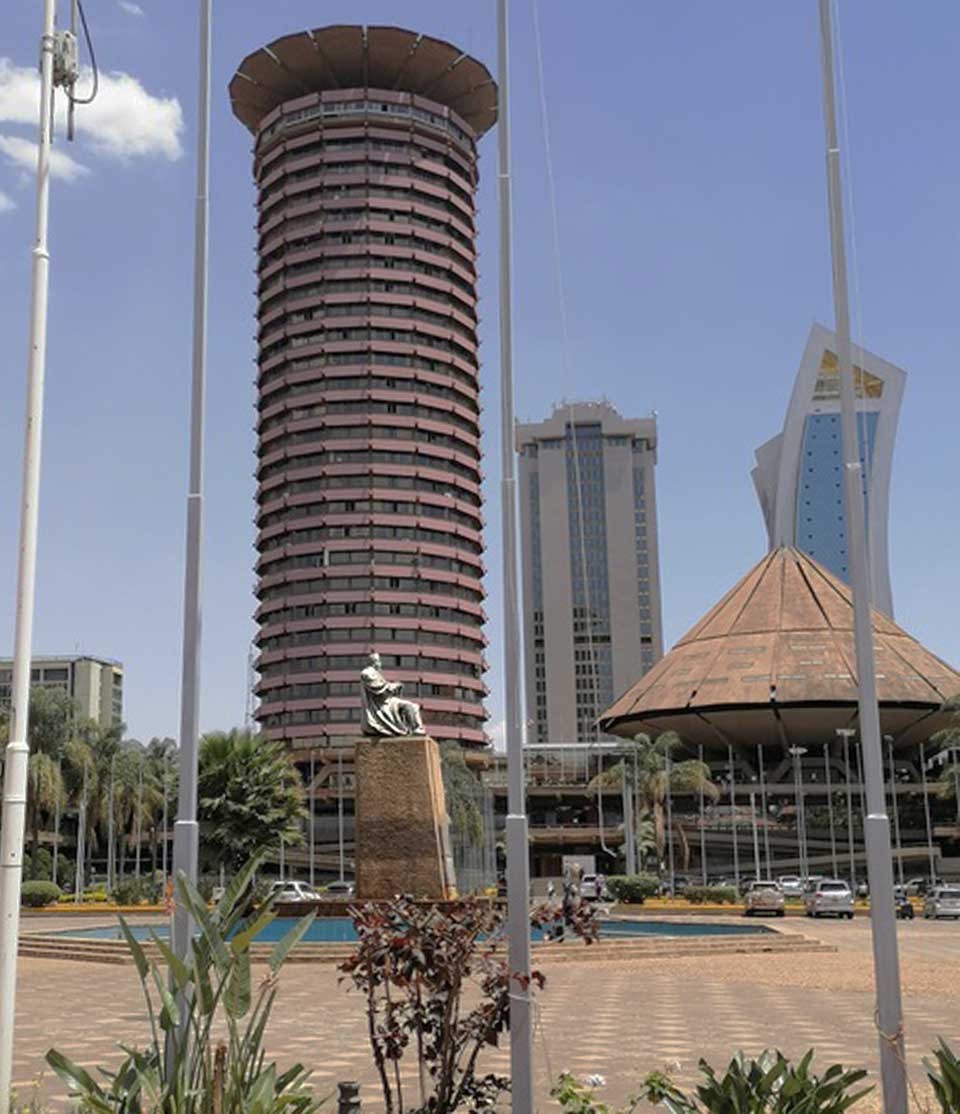

Figure 6 Kenyatta’s 1973 statue surrounded by the iconic Kenyatta International Convention Centre and Times Tower. © Lydia Muthuma
While the 1964 statue of Kenyatta was installed to mark the attainment of the country’s Republic status, (cf. figure 1.) it does not form the main subject of this article because of its inaccessibility to the ordinary Kenyan.The second statue of Jomo Kenyatta, which is the subject of this paper, was installed in City Square in 1973. Its situ (the 1973 statue) is about half a kilometer away from the Parliament buildings as shown in figure 4. It is curious that ten years after unveiling the first statue of Kenyatta (1964 to 1973) a second statue of the very same president was installed in City Square, near the first one. One wonders what prompted the erection of this second statue. Was the first lacking in any way? Because contemporaneous historical happenings do not supply a plausible answer, I turn to reasons artistic to account for the ‘double representation’ of Jomo Kenyatta.
City Square was designed in the 1930s as Nairobi’s most central public space. During this era, the colonial government was working hard to convince London that Nairobi could become the capital of a ‘federated’ East Africa with internal self rule. Kenya was to go the way of Australia or Canada within the British Empire. Nairobi Town Square (now City Square) was designed to show off the High Court (now Supreme Court). The visual focal point of Town Square was a statue of the then reigning monarch, King George V of Britain. But when the second world war signaled the beginning of the end of the British Empire, and the Mau Mau rebellion, similarly signaled the end of colonial rule in Kenya, the statue of King George V had to come down. Change in political leadership caused change in displaying of statues. Therefore from 1964, when this statue was dethroned, City Square was without a focal point – visually.
Even with the addition of the Kenyatta International Convention Centre (KICC) building, as a visual extension of the Supreme Court, the square still lacked visual balance and focal point. Thus in 1973, a second statue of Jomo Kenyatta was installed in order to solve this aesthetic problem. It took up the place that had borne King George V. The sculptor of this second statue, James Butler, was to fabricate work for a given site.It is in this sense that Kenyatta’s 1973 statue is considered site specific –the site was incomplete without the statue because previously it had held the statue of King George V, which was removed in c. 1963. Between 1963 and 1973, this spot was without a statue. Re-filling the gap, in this site, supplies a rationale for the repeated representation of Jomo Kenyatta –outside parliament in 1964 and in City Square in 1973; same person in the two statues.
Dedan Kimathi’s statue is not site specific: it was first fabricated then a site decided upon –later. In comparison to Kenyatta’s 1973 statue, Kimathi’s, while smaller in size, is provided with little, if any, viewing distance. It is placed amongst tall buildings at the intersection of two busy thoroughfares. However, whatever its artistic (de)merit, it comes with a wealth of historical re-imagining. Kimathi’s statue is considered an active element in the processes of decolonisation today. (Mwangi, E. 2010)
Again, unlike Kenyatta’s 1973 statue, Kimathi’s was not fashioned during his life time. It is posthumous since Kimathi was condemned to death by hanging, in 1956, for the crime of unlawful possession of a firearm. In reality though, his crime was rebelling against colonial rule as leader of the KLFA also known as the Mau Mau. The sentence was carried out in 1957 and his body deposited in an unmarked grave.Fifty years later – 1957 to 2007 – Kimathi’s statue was unveiled. The time lapse calls for a scrutiny and rationalization of ‘re-calling’ him from the dead. Why the need to represent him, by installing a statue, 50 years after his death? Political history is rife with explanations that are still on-going. (Julie MacArthur, 2019)
An artistic probing of Kimathi’s statue; if it brings back this Mau Mau hero to life and whether it was meant to, presents several challenges because the statue appears more symbolic than an actual re-presention of Kimathi. This is because of its size and situ. Its scale, in comparison to the adjacent built environment, is miniscule. It does not command viewership although it is right in the middle of the public. Its size renders it pedestrian and somewhat not worth more than a passing glance. There is little about it to catch the eye of a passerby. It can be mistaken for one more ‘live’ pedestrian attempting to cross the street. It is ‘camouflaged’ by its size which makes it blend into the pedestrian traffic. Its success, in engaging the viewer’s affects, is debatable. And a significant contributor is the statue’s site.Once Kimathi’s statue was completed, a decision was arrived at to install it at the junction of Kimathi and Mama Ngina Street, within busy vehicular and pedestrian traffic. Viewers are treated to snap shot sights of it amid the unending caravan of commuter buses. This style of ‘seeing’ is easily translated into a similar mode of remembering; snap shot, unclear memories of Kimathi – who was he again?
Conversely, in City Square, Jomo Kenyatta sits in the absence of interfering traffic; in the absence of impinging tall buildings and with ample viewing distance. Commendations like: “the statue (Kenyatta’s 1973) is an island by itself and can be approached from multiple areas both visually and physically which is a valuable status within space defining elements (…) It has the unmistakable character of an icon and can easily be the best defined statue in the country (Kenya),” are not unusual. Truly, the site of a statue influences the viewer’s response. http://www.archidatum.com/projects/jomo-kenyatta-statue-james-butler/
Conclusion
Perhaps because of the historical circumstances the two statues –Kenyatta’s 1973 and Kimathi’s 2007 are viewed differently. They also evoke varied responses. What cannot be overlooked is that their siting (situ) contributes to their visual perception, which in turn influences the remembrance and mental picture retained by the public.
The siting of both statues corresponds with Kenyatta being the central character in Kenya’s decolonisation narrative while Kimathi occupies the more peripheral position. Kenyatta (1973) sits in City Square while Kimathi is amid the hubbub of downtown Nairobi.
References
- http://www.archidatum.com/projects/jomo-kenyatta-statue-james-butler/
- Mwangi, E. (2010). The incomplete rebellion: Mau Mau movement in twenty-first-century Kenyan popular culture. Africa Today, 57(2), 86-113.
- Shanguhyia, M. S. (2019). Julie MacArthur, ed. Dedan Kimathi on Trial: Colonial and Popular Memory in Kenya’s Mau Mau Rebellion. Athens: Ohio University Press, 2017. xxvi+ 406 pp. Bibliography. Index. Paper. ISBN: 978-0896-803176. African Studies Review, 62(2), E12-E15.
published October 2020







