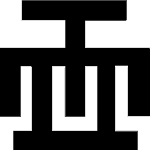|
|
Ese Ne Tekrema (The teeth and the tongue)
Symbol of generosity towards one another. Through the formation of a linear relationship in diversity towards a common goal, both the personal and societal needs of the people will be realized. |
 |
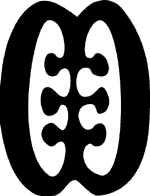
Funtumfunafu Denkyemfunafu (Siamese/conjoined crocodiles)
Symbol of brotherly feeling, caring and sharing. The society stays stronger when people coexist in the belief that we all smile and grow together when we feed and enjoy the good things in life together. |
 |
Dua Afe (Wooden comb)
Symbol of sanitation, cleanliness and beauty. This symbol reechoes the essence of physical and spiritual wellbeing through personal and environmental cleanliness. |
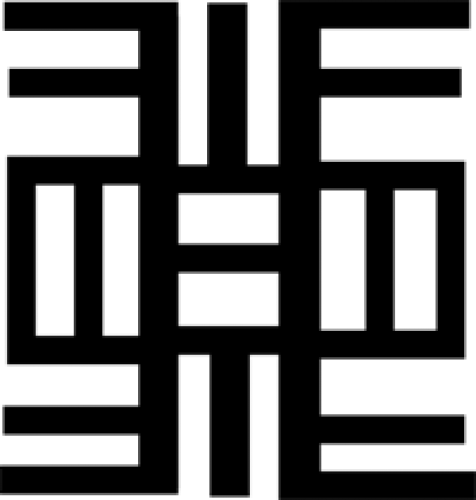 |
Nea Onnim No Sua a, Ohu (Anyone who does not know is capable of ‘knowing’ through education)
Symbol of educational opportunities. This symbol plays down ignorance by reminding people of their inert capabilities to get educated to any level of their preference. In other words, opportunities for quality education exist for all. |
 |
Obi Nka Bi (No one bites the other)
Symbol of equal regard, recognition and treatment for all. No one bites the other as a value ensures that all genders and age groupings have equal rights for existence in the society which allow them to listen and be listened. |
 |
Sesa Wo Suban (Change your life)
Symbol of deterrence and admonition towards all unapproved societal behaviors that affect the natural environment. This symbol represents strong advocacy for transformation and dynamic life patterns that affect nature. One of the unacceptable life patterns this symbol is currently addressing is the Ghanaian youth’s preference for wealth through illegal mining which destroys precious water bodies |
 |
Pempasie (Sew in readiness)
Symbol of production and sustainability. This symbol emphasizes the importance of societal preparedness and readiness for the future through effective production and management of all resources for posterity. |
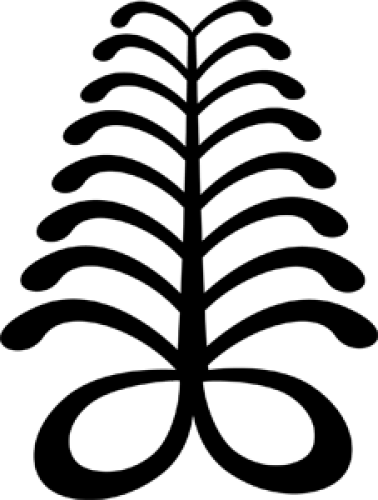 |
Aya (Fern)
Symbol of resourcefulness through resilience, self-reliance, hard work and judicious engagement of the environment and its resources.
|
 |
Nkyimkyim (Twisting)
Symbol of collective action towards the building of the human society through initiative, dynamism, versatility, innovation and resilience. Indeed, building a successful society, like life itself, is not a smooth journey. The journey of life is tortuous and it requires a great amount of innovation and creativity to sail through. |
 |
Nkonsonkonson (Chain)
A symbol of unity. This symbol, depicting two links in a chain, advocates for the need to heal the componentized society since in unity lies strength. |
 |
Eban (Fence)
A symbol of love, safety and security. The fence symbolically secures and protects the family from unhealthy activities outside of it. |
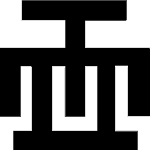 |
Hwehwe Mu Dua (Measuring stick)
Symbol of examination and Self/Quality Control. This symbol emphasizes the need for circumspection in all human endeavors. It directs attention to self and quality control in everything including production and consumption. It admonishes against over consumption, over production and all forms of egoistic instincts and behaviors which adversely affect the general good of the society.
|
 |
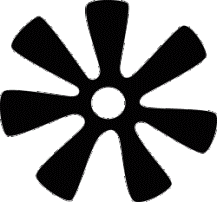
Nyame Biribi Wo Soro (God resides in the heavens)
Symbol of reverence to the heavens, the abode of the Supreme Being. Recognition to the ‘heavens’, or the skies as the residence of the supreme being is tied to the belief that all good things come from the heavens – rains, sunshine, fresh air, etc. The ‘heavens’ need to be respected for continuous flow of life-given goodies. |
 |
Ananse Ntentan (Spider’s Web)
Symbol of knowledge and wisdom about the complexities of life. This symbol alludes to the intricate personality of Ananse, the spider, a well-known character in Ghanaian/African folktales. In Ananse’s world, all facets of life need to be somehow manipulated, positively or negatively, for good or bad reasons. This sometimes led him to dire situation. Ananse therefore is a character for admonitions and reprimanding. Being conscious about the character of Ananse guides your steps against any unfair treatment to the world around you, be it the skies, on the land, in the waters or below the waters. |
 |
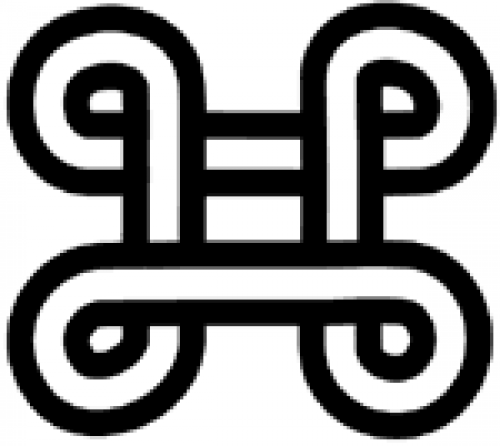
Asase Ye Duru (The Earth/Land is heavy)
Symbol for reverence and recognition to the providence and the divinity of the ‘Earth/Land’ and everything associated with it. The ‘Earth’ is the mother to everything. It carries the entire humanity, trees, water bodies, the sea (and what is in it and beneath it), big and small animals, etc. This why it is described as ‘heavy’. Respect/reverence to the Land is respect/reverence to life. |
 |
Mpatapo (Knot of Pacification/Reconciliation)
Symbol of bonding and adjudicatory factor which brings back parties in a dispute to a peaceful, harmonious and reconciliatory coexistence to ensure unified and strong societies and institutions. |
 |
Ti Koro Nko Agyina (One Head does not forma Council)
Symbol for partnership, collaboration and teamwork. This symbol emphasizes the importance of cooperation and collective efforts in the realization of all goals. Obviously, the attainment of the SDGs is a collective responsibility. No one nation (one head) can make it happen. It takes the concerted efforts of the entire citizenship of the world. |